Piano Sheets > Franz Schubert Sheet Music > Die Forelle (the Trout) (ver. 1) Piano Sheet
Die Forelle (the Trout) (ver. 1) by Franz Schubert - Piano Sheets and Free Sheet Music

About the Song
"Die Forelle" ("The Trout") Op.32 (D.550) is a lively lied written in 1817 by Franz Schubert (1797-1828). This immensely popular piece is for solo voice and piano. The lyrics are from the first three (of four) stanzas of a poem by Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart. The piece is written with a Varied Strophic structure, meaning the "verse music" is generally the same, with one different verse.
The song is the basis of a set of variations in the fourth movement of Schubert's Trout Quintet (D.667) which dates from 1819.
In 1846 it was transcribed and paraphrased by Franz Liszt in two versions for solo piano. Franz Peter Schubert (German pronunciation: [ˈfÊants ˈʃuËbÉ›É̯t]; January 31, 1797 – November 19, 1828) was an Austrian composer.
Although he died at an early age, Schubert was tremendously prolific. He wrote some 600 Lieder, nine symphonies (including the.
Download this sheet!
About the Artist
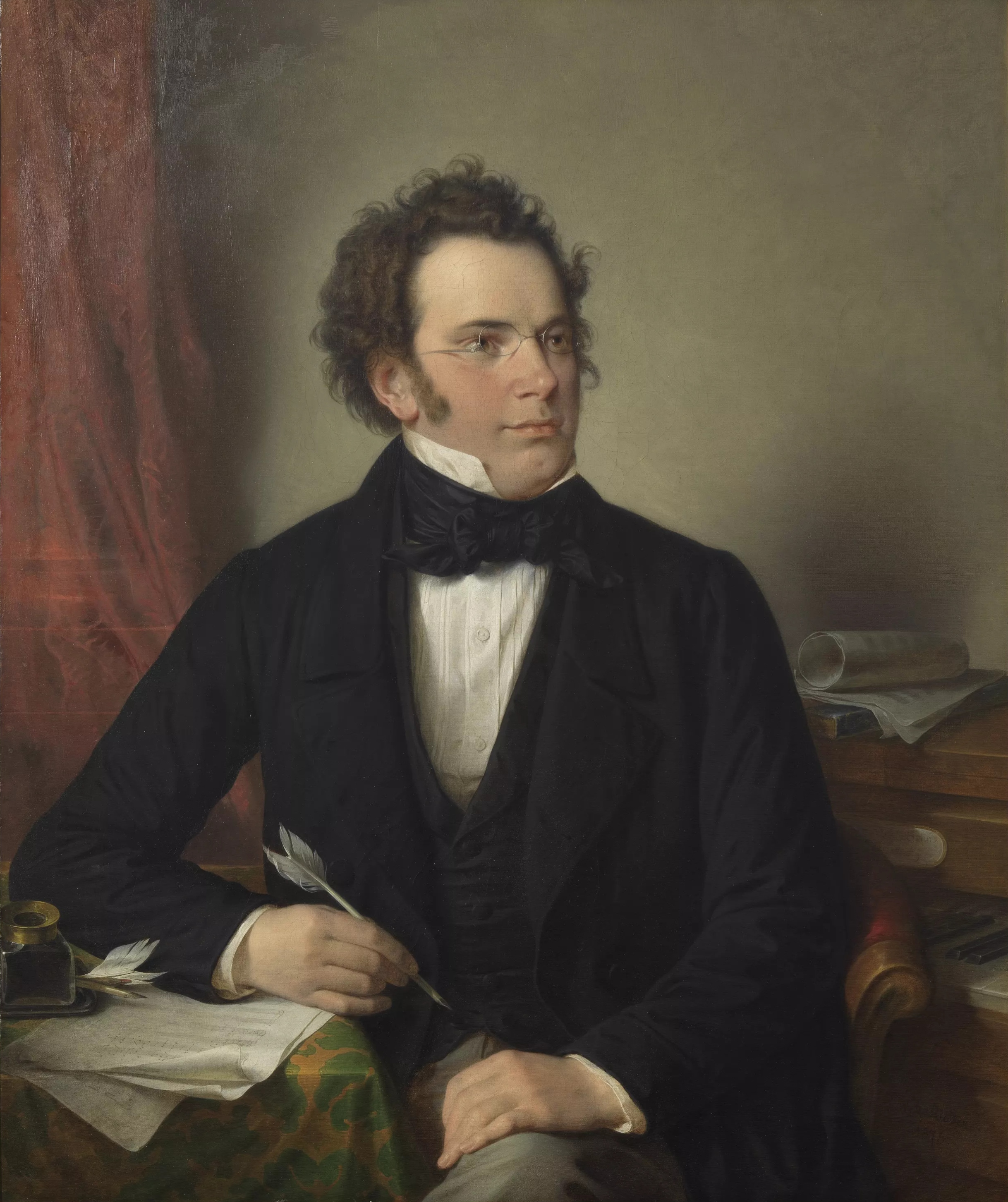
Random article
Sheet Music - Purpose and use Sheet music can be used as a record of, a guide to, or a means to perform, a piece of music. Although it does not take the place of the sound of a performed work, sheet music can be studied to create a performance and to elucidate aspects of the music that may not be obvious from mere listening. Authoritative musical information about a piece can be gained by studying the written sketches and early versions of compositions that the composer might have retained, as well as the final autograph score and personal markings on proofs and printed scores.
Comprehending sheet music requires a special form of literacy: the ability to read musical notation. Nevertheless, an ability to read or write music is not a requirement to compose music. Many composers have been capable of producing music in printed form without the capacity themselves to read or write in musical notation—as long as an amanuensis of some sort is available. Examples include the blind 18th-century composer John Stanley and the 20th-century composers and lyricists Lionel Bart, Irving Berlin and Paul McCartney.
The skill of sight reading is the ability of a musician to perform an unfamiliar work of music upon viewing the sheet music for the first time. Sight reading ability is expected of professional musicians and serious amateurs who play classical music and related forms. An even more refined skill is the ability to look at a new piece of music and hear most or all of the sounds (melodies, harmonies, timbres, etc.) in one's head without having to play the piece.
With the exception of solo performances, where memorization is expected, classical musicians ordinarily have the sheet music at hand when performing. In jazz music, which is mostly improvised, sheet music—called a lead sheet in this context—is used to give basic indications of melodies, chord changes, and arrangements.
Handwritten or printed music is less important in other traditions of musical practice, however. Although much popular music is published in notation of some sort, it is quite common for people to learn a piece by ear. This is also the case in most forms of western folk music, where songs and dances are passed down by oral—and aural—tradition. Music of other cultures, both folk and classical, is often transmitted orally, though some non-western cultures developed their own forms of musical notation and sheet music as well.
Although sheet music is often thought of as being a platform for new music and an aid to composition (i.e., the composer writes the music down), it can also serve as a visual record of music that already exists. Scholars and others have made transcriptions of western and non-western musics so as to render them in readable form for study, analysis, and re-creative performance. This has been done not only with folk or traditional music (e.g., Bartók's volumes of Magyar and Romanian folk music), but also with sound recordings of improvisations by musicians (e.g., jazz piano) and performances that may only partially be based on notation. An exhaustive example of the latter in recent times is the collection The Beatles: Complete Scores (London: Wise Publications, c1993), which seeks to transcribe into staves and tablature all the songs as recorded by the Beatles in instrumental and vocal detail. (More...)
